Security Basic 2
Computer Security Concepts
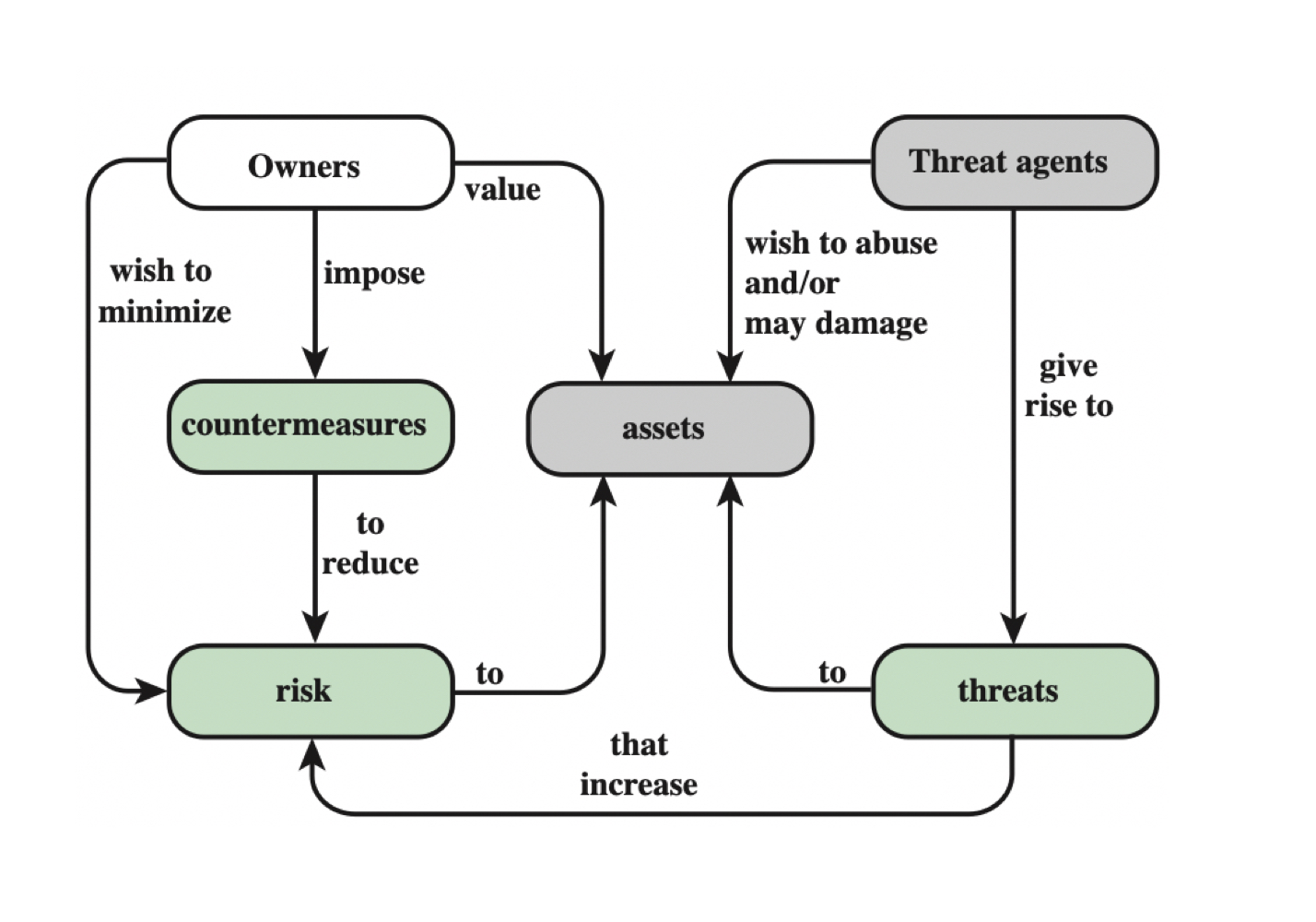
- Asset
- Vulnerability
- Threat
- Attack
- Countermeasure or control
Asset
Things might want to protect
- Hardware: Includeing computer systems and other data processing, data storage.
- Software: Including the operating system, system utilities, and applications.
- Data: Including files and databases, as well as security-related data.
   ex) password files - Communication facilities and networks: Local and wide area network communication links, bridges, routers, and so on.
Vulnerabilities
Weaknesses or gaps in the security system that could be exploited to cause loss or harm.
Weakness can be occur through flaws`, features or user error, and attackers will look to exploit any of them, often combining one or more, to achieve their end goal.
Flaws
- It is an unitended funcitonality. This may either be a result of poor design or through mistakes made during implementation. Flaws may go undetected for a significant period of time. The majority of common attacks we see today exploit these types of vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerabilities are actively pursued and exploited by the full range of attackers consequently, a market has grown in software flaws, with “zero-day” vulnerabilities fetching hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Examples
- A file server that doesn’t authenticate its users
- Bad passwords
- Buggy software
- Untrained employees
- Lack of encryption
Categories
- Corrupted (Loss of integrity): The system can be corrupted, so it does the wrong thing or gives wrong answers.
  ex) Stored data values may differ from what they should be because they have been improperly modified. - Leaky (Loss of confidentiality): The system can be leaky.
  ex) Someone who should not have access to some or all of the information available through the network obtains such access. - Unavailable or very slow (Loss of availability): The system can become unavailable or very slow.
  -> using the system or network becomes impossible or impractical.
Threats
Threats are potentials for vulnerabilities to turn into attacks on systems. Threats are potential dangers or harmful events that could exploit vulnerabilities in a system or organization, leading to negative impacts.
Attacks
An action which explits a vulnerability to execute a threat.
Attacks (threats carried out) lead to compromises or security breaches.
Can be classified as Passive and Active.
*Passive: Attempt to learn or make use of information from the system that does not affect system resources.
*Active: Attempt to alter system resources or affect their operation.
Also be classified based on the source/origin of the attacks, Inside attack and Outside attack.
*Inside attack: Initiated by entity with authorized access to system.
*Outside attack: Initiated by unauthorized user of the system.
Example
- Telling the file server you are a different user in an attempt to read or modifiy their files are ways to exploiting a vulnerability to damage assets.
- Bad passwords: using password crackers
- Buggy software: launching an SQL injection attack
- Untrained employees: tricking them to share their credentials
- Lack of encryption: eavesdropping on communications
Risk
The potential for loss, damage or destruction of an asset as a result of a threat exploiting a vulnerability.
It is the likelihood that a threat will exploit a vulnerability to cause damage to an asset.
Combination of the potential impact and the probability of a threat occurring.
Example
- Financial losses
- Loss of privacy
- Damage to your reputation
- Legal implications
- Even loss of life
Reference
- CS458-Introduction to Information Security. (2024). Sajad Meisami, Ph.D. Illinois Institute of Technology.
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: