Growth of Function - Big O
There exists a relation between the input data size (\(n\)) and the number of operations performed (\(N\)) with respect to time. This relation is denoted as the Order of growth in time complexity and given notation \(O(n)\) where ‘\(O\)’ is the order of growth and \(n\) is the length of the input. It is called Big O Notation. Big O notation expresses the run time of an algorithm in terms of how quickly it grows relative to the input \(n\) by defining the $N$ number of operations that are done on it. Also, the time complexity of an algorithm is denoted by the comvination of all \(O(n)\) assigned for each line of function. Big O notation is the prevalent notation to represent algorithmic complexity. It gives an upper bound on complexity and hence it signifies the worst-case performance of the algorithm. With such a notation, it’s easy to compare different algorithms because the notation tells clearly how the algorithm scales when input size increases. This is often called the order of growth.
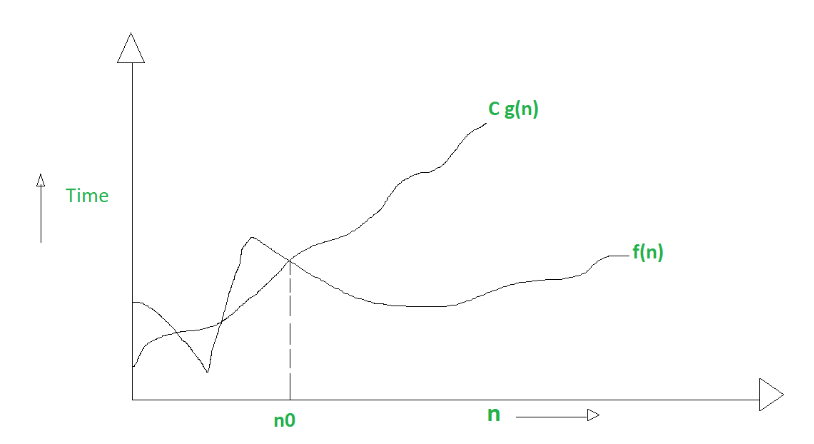
Let \(f\) and \(g\) be functions from the set of integers or the set of real numbers to the set of real numbers We say that \(f(x)\) is \(O(g(x))\) if there exist positive constants \(C\) and \(k\) such that:
> \(|f(x)| \leq C|g(x)|\)
whenever \(x > k\). This is read as “\(f(x)\) is big-oh of \(g(x)\).”
In other words, when \(x\) is large enough, \(f(x)\) is upper bounded by a constant time of \(g(x)\). Big-O notation is also called the asymptotic upper bound of a function. If a function is \(O(n)\), it is automatically \(O(n^2)\).
The following graph is the example for Big-O.
Types of Time Complexity
\(O(1)\) - Constant time
When an algorithm is not dependent on the input size $n$. If an algorithm’s time complexity is constant, it means that it will always run in the same amount of time, no matter the input size.
Example
- If we want to get the first item of an array, it does not matter how big the input size is. It always takes the same amount of time to find the first element in the array.
- Find if a number is odd or even
- Check if an item on an array is null
- Print the first element from a list
- Find a value on a map
\(O(n)\) - Linear time
When the running time increases linearly with the length of the input, an algorithm is a linear time complexity. When the function involves checking all the values in input data, with \(O(n)\).
Example
- Get the max/min value in an array
- Find a given element in a collection
- Print all the values in a list
\(O(log n)\) - Logarithmic time
When an algorithm reduces the size of the input data in each step. This indicates that the number of operations is not the same as the input size. The number of operations gets reduced as the input size increases. This time complexities usually apply to algorithms that divide problems in half every time.
Example
- Finding element on sorted array with binary search
\(O(n^2)\) - Quadratic time
An algorithm is said to have a non-linear time complexity where the running time increases non-linearly with the length of the input. Nested loops come under this order where one loop takes \(O(n)\) and if the function involves a loop within a loop, then it goes for \(O(n) \times O(n) = O(n^2)\) order.
Example
- Check if a collection has duplicated values
- Sorting items in a collection using bubble sort, insertion sort, or selection sort.
- Find all possible ordered pairs in a array.
\(O(2^n)\)
Growth doubles with each addition to the input data set. The growth curve of an \(O(2^n)\) function is exponential - starting off very shallow, then rising meteorically. \(O(2^n)\) complexities are often seen in recursive functions that make 2 recursive calls and pass in the problem size of \(n - 1\).
Example
- The recursive calculation of Fibonacci numbers.
- Tower of Hanoi
Compare
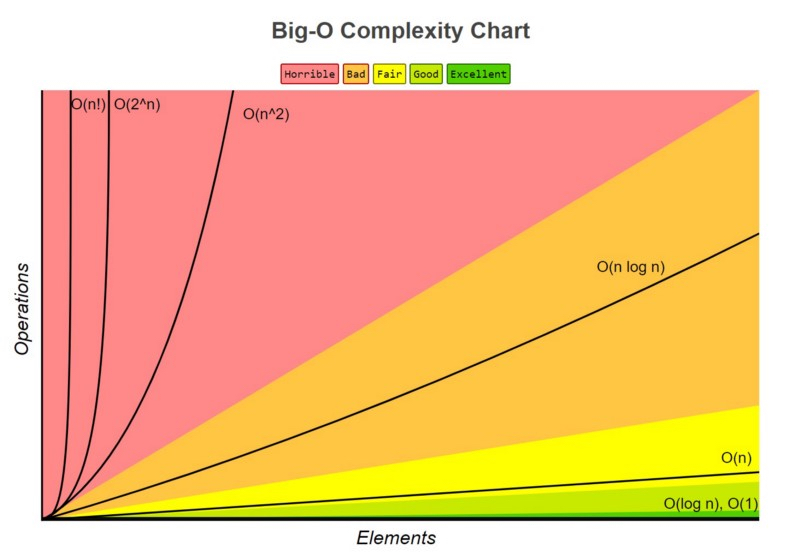
\[O(1) < O(log n) < O(\sqrt n) < O(n) < O(nlogn) < O(n^2) < O(n^3) < O(10^n) < O(n!)\]Example
-
Show that \(f(n) = 4n^2 - 4\) is \(O(n^2)\).
-> can choose \(k = 1\) and \(C = 4\) (there are infinite choices of \(k\) and \(C\)). When \(n > 1\), we have \(4n^2 -4 \le 4n^2\). -
Show that \(f(n) = 4n^2 - 4\) is not \(O(n)\).
-> Prove by contradiction. If \(4n^2 - 4\) is \(O(n)\), then there exist positive constants \(k\) and \(C\) such that “if \(n > k\), then \(4n^2 - 4 \le Cn\). When \(n > 0\), we can divide both sides of the inequality by \(n\) and we get: \(4n - \frac {4}{n} \le C\), which implies that \(4n \le C + \frac {4}{n} < C + 4\). Since \(C + 4\) is a constant, \(4n < C + 4\) cannot hold for all \(n > k\). In particular, if \(n > max\){\(k, \frac{C+4}{4}\)}, it is not true that \(4n < C + 4\). This contradiction shows that $n^2$ is not \(O(n)\).
Complexity Chart
Data Structure
| Data Structures | Space Complexity | Average Case Time Complexity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Access | Search | Insertion | ||
| Array | \(O(n)\) | \(O(1)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n)\) |
| Stack | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(1)\) |
| Queue | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(1)\) |
| Single Linked List | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(1)\) |
| Double Linked List | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(1)\) |
| Hash Table | \(O(n)\) | N/A | \(O(1)\) | \(O(1)\) |
| BST | \(O(n)\) | \(O(logn)\) | \(O(logn)\) | \(O(logn)\) |
Search Algorithm
| Search Algorithms | Space Complexity | Time Complexity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best Case | Average Case | Worst Case | ||
| Linear Search | \(O(1)\) | \(O(1)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n)\) |
| Binary search | \(O(1)\) | \(O(1)\) | \(O(logn)\) | \(O(logn)\) |
Sorting Algorithm
| Sorting Algorithms | Space Complexity | Time Complexity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best Case | Average Case | Worst Case | ||
| Selection Sort | \(O(1)\) | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n^2)\) | \(vO(n^2)\) |
| Insertion Sort | \(O(1)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n^2)\) |
| Bubble Sort | \(O(1)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n^2)\) |
| Quick Sort | \(O(logn)\) | \(O(logn)\) | \(O(logn)\) | \(O(logn)\) |
| Merge Sort | \(O(n)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(logn)\) | \(O(logn)\) |
| Heap Sort | \(O(1)\) | \(O(1)\) | \(O(logn)\) | \(O(logn)\) |
Reference
- CS 430, Introduction to Algorithm, prof. Wang, Xiaolang, Spring 2023, Illinois Institute of Technology
- Design and analysis of algorithms (2022) GeeksforGeeks. GeeksforGeeks. Available at: geeksforgeeks.
- Team, G.L. (2022) What is time complexity and why is it essential?, Great Learning Blog: Free Resources what Matters to shape your Career! Available at: mygreatlearning.com.
- Dineshpathak, A. (2022) Algorithmic complexity, Devopedia. Devopedia Foundation. Available at: devopedia.org.
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: