Stack
Stack
Stack is an Abstract Data Type that serves as a collection of elements. Also, stack is a linear structure. Java do provide the stack class under ‘Java.util’ package. We can use it easily using ‘import’.

Definition of Stack
A pile of something, usually neatly arranged
A structure in which elements are added and removed from only one end; “Last in, First out” (LIFO) structure.
Operations on Stack
- Constructor
- new: creates an empty stack
- Transformers
- push
- pop
- Observer
- top (or peek)
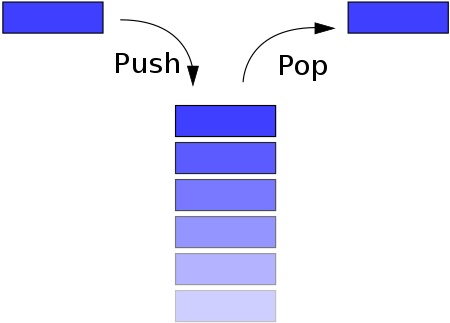
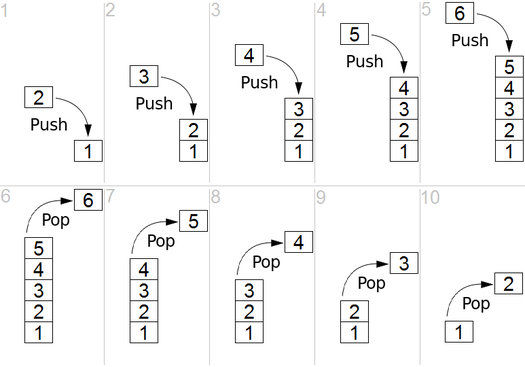
Usage of Stack
Stack is often used for ‘system’ programming.
- To keep track of sequences of operation calls
- Compilers use stacks to analyze nested language statements
- Operating systems save information about the current executing process on a stack, so that it can work on a higher-priority, interrupting process.
Methods
-
push: Add an item onto the top of this stack.
public void push(T element) throws StackOverflowException { if (isFull()) // Throw 'StackOverflowException' if this stack is FULL. throw new StackOverflowException("Push attempted on a full stack."); else { // If not, add element at the top of this stack. topIndex++; elements[topIndex] = element; } } -
pop: Removes the object at the top of this stack. It throws exception, if this stack is empty.
public void pop() throws StackUnderflowException { if (isEmpty()) // Throw 'StackUnderflowException' if this stack is EMPTY. throw new StackUnderflowException("Pop attempted on empty stack."); else { elements[topIndex] = null; topIndex--; } } -
top (or peek): Looks at the object at the top of this stack without removing it from the stack. This method also throws exception, if this stack is empty.
public T top() throws StackUnderflowException { T topStack = null; if (isEmpty()) // Throw 'StackUnderflowException' if this stack is EMPTY. throw new StackUnderflowException("Top attempted on empty stack."); else topStack = elements[topIndex]; // Return top element of this stack. return topStack; } - isEmpty: Returns true if this stack has nothing. Otherwise, false.
public boolean isEmpty() { // Return true if this stack is empty. return (topIndex == -1); } -
search: Returns the 1-based position where an object is on this stack. Returns ‘-1’ if the object does not on the stack.
public int search(T value) { for (int index = topIndex -1; index >= 0; index--) { // If found the value, returns the position of the value in this stack. if (elements[index].equals(value)) return topIndex - index; } // If not, returns -1. return -1; }
Full Code
public class ArrayStack<T> implements StackInterface<T> {
protected final int DefCap = 50; // Set 50 as default capacity
protected T[] elements; // Storage of stack elements
protected int topIndex = -1; //Index of top element in this stack. If this stack is empty, 'topIndex' is -1.
// Constructor
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ArrayStack() {
elements = (T[]) new Object[DefCap];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ArrayStack(int max) {
elements = (T[]) new Object[max];
}
// Transformers
public void push(T element) throws StackOverflowException {
if (isFull()) // Throw 'StackOverflowException' if this stack is FULL.
throw new StackOverflowException("Push attempted on a full stack.");
else { // If not, add element at the top of this stack.
topIndex++;
elements[topIndex] = element;
}
}
public void pop() throws StackUnderflowException {
if (isEmpty()) // Throw 'StackUnderflowException' if this stack is EMPTY.
throw new StackUnderflowException("Pop attempted on empty stack.");
else {
elements[topIndex] = null;
topIndex--;
}
}
// Observer
public T top() throws StackUnderflowException {
T topStack = null;
if (isEmpty()) // Throw 'StackUnderflowException' if this stack is EMPTY.
throw new StackUnderflowException("Top attempted on empty stack.");
else
topStack = elements[topIndex];
// Return top element of this stack.
return topStack;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
// Return true if this stack is empty.
return (topIndex == -1);
}
public boolean isFull() {
// Return true if this stack is FULL.
return (topIndex == elements.length - 1);
}
public int search(T value) {
for (int index = topIndex -1; index >= 0; index--) {
// If found the value, returns the position of the value in this stack.
if (elements[index].equals(value))
return topIndex - index;
}
// If not, returns -1.
return -1;
}
}
Complexity of Stack (Big-O)
The Complexity of the stack is O(1). Because we do not run ‘loop’ function in the push, pop, peek, and empty operations which is basic operation of stack without search operation. The complexity of search operation is O(n).
Applications of Stack
- Balancing of symbols
- Infix to Postfix or Prefix conversion
- Redo-undo features in many programs such as MS office, editors, photoshop.
- Forward and backward feature in web browsers.
- In many algorithms such as Tower of Hanoi, tree traversals, stock span problem, histogram problem.
- Backtracking is one of the algorithm designing techniques. Such as Knight-Tour problem, N-Queen problem, chess, maze.
- In graph algorithms (Topological Sorting and Strongly Connected Components).
- In memory management. Any modern computer uses a stack as the primary management for a running purpose. Each program that is running in a computer system has its own memory allocations.
Implementation
Array and Linked List
Reference
- CS401-Data Structure. (2021). Micheal Y. Choi, Ph.D. Illinois Institute of Technology.
- GeeksforGeeks. (2021, September 17). Stack Data Structure (Introduction and Program). geeksforgeeks
- Stack (Java Platform SE 7 ). (2020, June 24). Oracle. oracle.com
- Stack (abstract data type). (2021, December 30). In Wikipedia. wikipedia
https://github.com/namdarine/DataStructure.git
StackInterface, StackOverflowException, StackUnderflowException, Array Stack, and Linked List Stack codes are uploaded in ‘Stack’ package inthis github repository.
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: