A.I. Intro - Agent
Most A.I. problems will exhibit the following three characteristics
- tend to be large
- computationally complex and cannot be solved by a straightforward algorithm
- tend to require a significant amount of human expertise to be solved
Interlligent (Autonomous) Agent
Agent
An agent is just something that acts (from the Latin agere, todo) “Acting” to be
- autonomous
- situated in some environment (that could be really complex)
- adaptive
- creative and goal-oriented
Rational Agent
One that acts so as to achieve the best outcome, or when there is unvertainty, the best expected outcome.
AI is focused on the study and construction of agents that do the right thing.
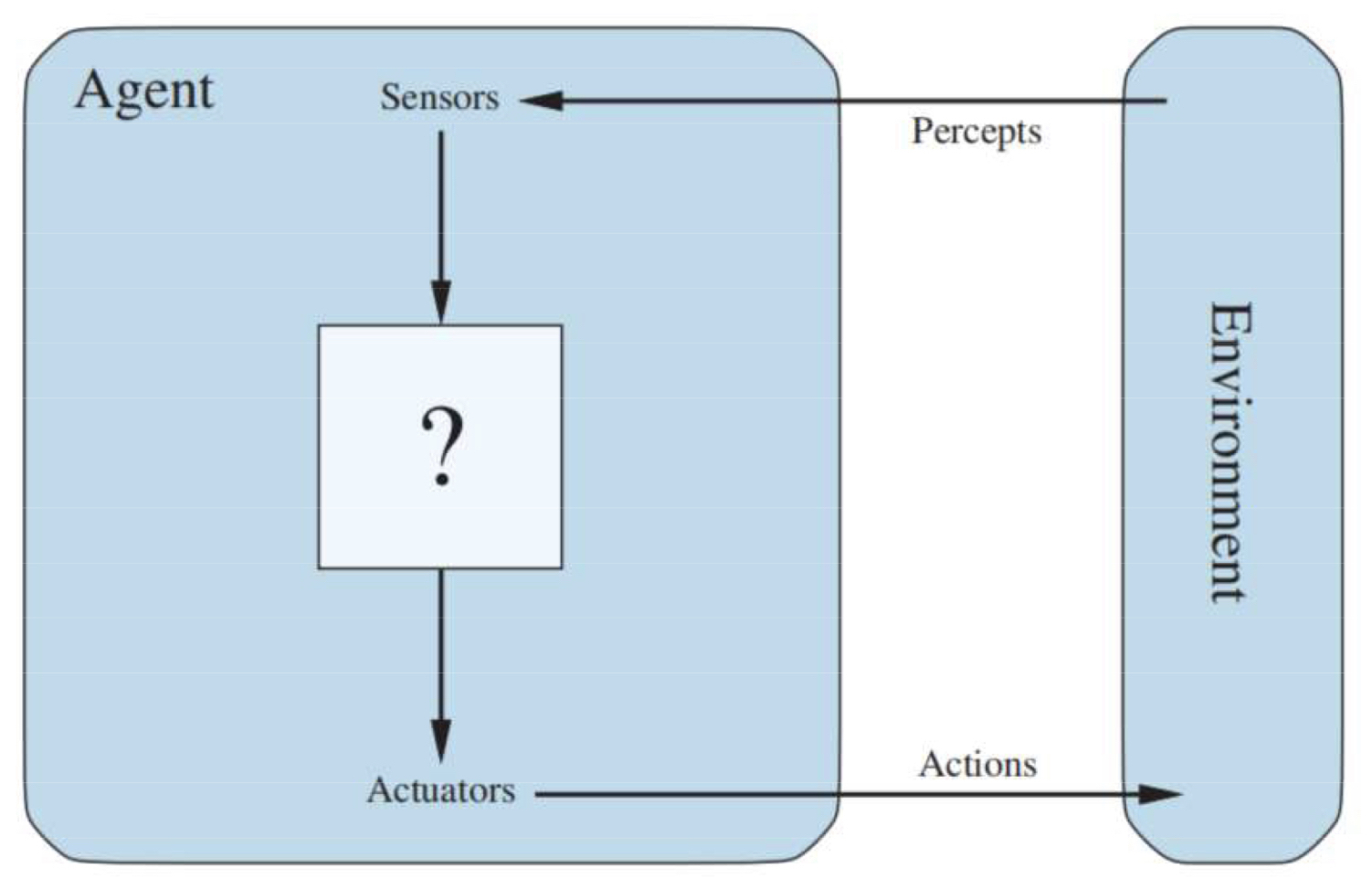
An agent is anything that can be viewed as perceiving its environment through sensors and acting upon that environment through actuators.
- Percept: content / information that agent’s sensors are perceiving / capturing currently
- Percept Sequence: a complete history of everything that agent has ever perceived.
- any practical issues that you can see here?
- what can a percept sequence be used for?
Agent’s choice of action / decision at any given moment.
- CAN depend on:
- built-in knowledge
- entire percept ssequence
- CANNOT depend anything it hasn’t perceived
Agent’s action CAN change the environment state
Agent Function / Program
- Specifying an action choice for every possible percept sequence would define an agent
- Action <-> percept sequence mapping is the agent function
- Agent function describes agent behavior
- Agent Function is an abstract concept
- Agent program implements agent function
Actions have consequences
- An agent can act upon its environment, but how do we know if the end result is “right”?
- After all, actions have consequences: either good or bad.
- Recall that agent actions change the environment state
- If state changes are desirable, and agent performs well.
- performance measure evaluates state changes. -> It is better to design performance measures according to what one actually want to be achieved in the environment, rather than according to how one thinks the agent should behave. -> Warning: If it is difficult to specify the performance measure, agents may end up optimizing a wrong objective. Handle uncertainty well in such cases.
Example of Agent
- A software agent has Keystrokes, file contents, received network packages which act as sensors and displays on the screen, files, and sent network packets acting as actuators.
- A Human-agent has eyes, ears, and other organs which act as sensors, and hands, legs, mouth, and other body parts act as actuators.
- A Robotic agent has Cameras and infrared range finders which act as sensors and various motors act as actuators.
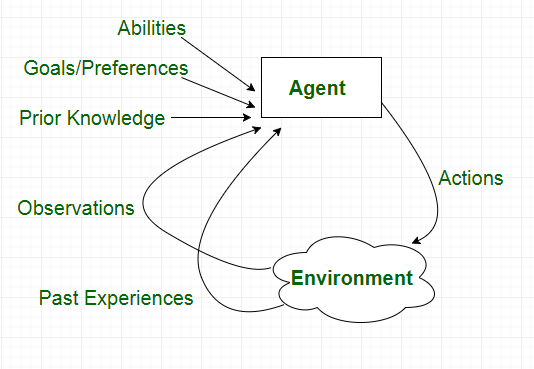
Rationality
Rational decisions at the moment depend on:
- The performance measure that defines success criteria
- The agent’s prior knowlege of the environment
- The actions that the agent can perform
- The agent’s percept sequence so far
Rational Agent
-> For each possible percept sequence, a rational agent shoud select an action that is expected to maximize its performance measure, given the evidence provided by the percept sequence and whatever built-in knowledge the agent has. A rational agent could be anything that makes decisions as a person, firm, machine, or software. It carries out an action with the best outcome after considering past and current percepts (agent’s perceptual inputs at a given instance). To determine the rational agent, we need to say what the performance measure is, what is known about the environment, and what sensors and actuators the agent has.
Rationality in Reality
- An omniscient agent will ALWAYS know the final outcome of its action. Impossible in reality. That would be perfection.
- Rationality maximizes what is EXPECTED to happen
- Perfection maximizes what WILL happen
- Performance can be improved by information gathering and learning
Reference
- Illinois Institue of Technology CS480 (Intro Artificial Inteligence) Fall 2022 prof. Jacek Dzilkowski
- Agents in Artificial Intelligence. (2018, January 28). GeeksforGeeks. geeksforgeeks
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: